 |
1 Apparatus Models and their Parameters |
|
 |
|
|
|
Park model including one amortisseur circuit in the q-axis and the d-axis was used for modeling the generators (the parameters used for the generators themselves are the same as the standard parameters of the Y-method). |
|
|
|
 These parameters are listed in Table 1.1. These parameters are listed in Table 1.1. Table 1.1 Generator Constants. |
|
|
 |
1.1 Excitation Models |
|
 |
|
|
|
The following 3 types of the excitation models have been considered. |
|
|
|
 Rotating type excitation model (LAT = 1) Rotating type excitation model (LAT = 1)
 Thyristor excitation model (LAT = 2) Thyristor excitation model (LAT = 2)
 Thyristor excitation model equipped with DP type PSS (LAT =102) Thyristor excitation model equipped with DP type PSS (LAT =102)
LAT means ID number of standard AVR type used in CRIEPI’s Y-method. The simplified PSS constants is decided to damp the long term swing (period = 1 – 4 [sec]).
 Fig. 1.1 shows the block diagram used and the parameters. Fig. 1.1 shows the block diagram used and the parameters.
 Fig.1.1 Excitation Models |
|
|
 |
1.2 Governor Models |
|
 |
|
The following 3 types of the governor models have been considered |
|
 Thermal and Nuclear Plants Governor System Model (LPT = 1) Thermal and Nuclear Plants Governor System Model (LPT = 1)
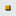 Hydraulic Plants Governor System Model I (LPT = 3) Hydraulic Plants Governor System Model I (LPT = 3)
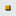 Hydraulic Plants Governor System Model II (LPT = 4) Hydraulic Plants Governor System Model II (LPT = 4) |
|
LPT means ID number of standard governor type used in CRIEPI’s Y-method. Fig. 2 shows the block diagram and the parameters.
Fig.1.2 Governor Models
The unit of the turbine output is MW base. (When the active power output [MW] is the rated, the turbine output is 1 [pu].)
Fig.1.3 Operation Modes |
|
|
 |
1.3 Step-Up Transformer |
|
 |
|
The value of the transformer’s reactance is 0.14 p.u. on machine base. However, the zero impedance is neglected. |
|
|
 |
1.4 Transmission Lines Models |
|
 |
|
|
|
The transmission lines are represented by the equivalent p circuits. The impedance used is a standard impedance in a 500 kV system of 4 conductors (TACSR 810 mm2 ).
The values of the impedance of a single line, 100 km are given below. The base values are 1000 MVA, 500 kV. |
|
|
|
50 Hz System (1000MVA, 500kV base, 1 cct. /100km)
Impedance: Z= r+jX = 0.0046+j0.1068 [p.u.]
Electrical charge capacity: jY/2 = 0.0538 [p.u.]
60 Hz System (1000MVA, 500kV base, 1 cct. /100km)
Impedance: Z= r+jX = 0.0042+j0.1262 [p.u.]
Electrical charge capacity: jY/2 = 0.0610 [p.u.]
The zero impedance of the transmission line was not considered. |
|
|
 |
1.5 Load Models |
|
 |
|
|
|
The load characteristics were based on past measurements. When the voltage is about 1 p.u., the active power is represented as a constant current. When the voltage is below a certain value, the active power is represented as constant impedance. Under the entire domain of the voltage, the reactive power is represented as constant impedance.
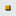 Fig.1.4 Load model (NLT = 2)
However, this load characteristic NLT = 2 is not continuously changed at the load voltage V = 0.7 [pu] .
The following Load characteristic (NLT = 107) is continuously changed between the constant current and the constant impedance characteristic at V = 0.7.
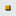 Fig.1.5 Load model (NLT = 107) |